- 1置顶帖 - 本帖收集增加的内容公开
- 2python - 介绍公开
- 3python安装 - 在线安装公开
- 4python安装 - 离线安装公开
- 5自带库 - pip - 管理python包工具公开
- 6自带库 - pip - 离线安装pip、python包公开
- 7版本控制 - 多python、多pip(2/3) - 各系统版本控制公开
- 8环境配置 - Python + VSCode公开
- 9环境配置 - Python + Pycharm公开
- 10环境配置 - .gitignore文件例子公开
- 11结构分配 - 建议的结构分配公开
- 12语法 - if __name__ == "__main__" - 程序入口公开
- 13语法 - from .aa.bb import cc - 导入模块公开
- 14语法 - __init__.py - python包标识公开
- 15语法 - class xx: - 类公开
- 16语法 - class BB(AA): - 类 - 有继承公开
- 17语法 - def XXX(参数1,参数2): - 定义方法公开
- 18语法 - def __XXX(参数1,参数2): - 定义私有属性方法公开
- 19语法 - 类 - (*args, **kwargs) - 元祖、字典公开
- 20装饰器 - @property - 类 - 方法只读公开
- 21装饰器 - @staticmethod - 类 - 静态方法公开
- 22装饰器 - @classmethod - 类 - 可以找类参数公开
- 23装饰器 - 普通装饰器 - @add公开
- 24装饰器 - 带参数装饰器 - @add(id="123")公开
- 25语法 - .__xx__()魔法方法 - 直接使用公开
- 26语法 - def __xx__()魔法方法 - 需要自己定义公开
- 27语法 - def __xx__()魔法方法 - 可以重写、其他公开
- 28数据类型 - int整数 - 1 - +加 -减 *乘 /除公开
- 29数据类型 - float浮点数 - 1.0 - +加 -减 *乘 /除公开
- 30数据类型 - string字符串 - "A" - replace()公开
- 31数据类型 - string字符串 - "A" - global公开
- 32数据类型 - 格式化 - string、int、float - %s %d %f公开
- 33数据类型 - List列表 - l = [1,2,3] - 操作公开
- 34数据类型 - tuple元组 - l = (1,2,3) - 不可增删改公开
- 35数据类型 - dict字典 - d = {"A":"a",} - 操作公开
- 36数据类型 - JSON - j = {"A":"a",} - 操作公开
- 37自带方法 - data[ ] - 切片公开
- 38自带方法 - print(pay.__dict__)打印obj内容公开
- 39自带方法 - open() - 读写文件公开
- 40自带方法 - t = type(xxx) - 查数据格式公开
- 41自带方法 - l = len(xx) - 长度 ->int格式公开
- 42自带方法 - name = input() - 终端输入公开
- 43自带方法 - isinstance (obj, classinfo) - 判断类型公开
- 44自带方法 - sorted() - 排序-可迭代的对象进行排序公开
- 45自带方法 - 规则.format(原始数据) - 格式化公开
- 46自带方法 - import - 导入包公开
- 47自带方法 - locals()["xx"] - 字典,全部局部变量公开
- 48自带方法 - getattr(a, "bar") - 获得属性值公开
- 49自带方法 - 其他自带方法公开
- 50转换 - bytes转string - b.decode()公开
- 51转换 - string转bytes - str.encode()公开
- 52转换 - string转list - list(string)公开
- 53转换 - tuple()元组 -互转- list[]列表公开
- 54转换 - list[]列表 -转- Dataframe df公开
- 55转换 - list[]列表 -转- dict{}字典公开
- 56转换 - dict{}字典 -转- list[]列表公开
- 57转换 - dict{}字典 -转- Dataframe df公开
- 58转换 - Dataframe df -转- dic{}字典公开
- 59转换 - [(),(),()] -转- DataFrame df公开
- 60语句 - 作用简介公开
- 61语句 - if xxx: else: - 判断有无,判断是否公开
- 62语句 - for d in data: - 循环修改/取数公开
- 63语句 - while - 循环公开
- 64语句 - try: except: - 尝试获得公开
- 65关键字 - with公开
- 66关键字 - return - 方法结束返回数据公开
- 67关键字 - raise - 方法失败返回异常公开
- 68自带库 - venv - 虚拟环境公开
- 69自带库 - os - 系统路径操作公开
- 70自带库 - sys - 关于python解释器操作公开
- 71自带库 - re - 正则匹配公开
- 72自带库 - time - 时间公开
- 73自带库 - datetime - 时间公开
- 74自带库 - math - 数学公开
- 75自带库 - ElementTree - XML操作公开
- 76自带库 - smtplib - 发信息公开
- 77自带库(3.5) - 异步asyncio - async,await关键字公开
- 78自带库 - copy - 复制、前复制、深复制公开
- 79自带库 - HMAC SHA256 加密公开
- 80自带库 - fcntl - 文件锁公开
- 81自带库 - mutiprocessing - 多进程公开
- 82自带库 - logging - 日志公开
- 83自带库 - urllib - 请求库公开
- 84第三方库 - 命令行工具 - you-get下载视频公开
- 85第三方库 - virtualenv - 虚拟环境公开
- 86第三方库 - pipdeptree - 包的依赖关系公开
- 87第三方库 - PyExecJS - 调用JavaScript公开
- 88第三方库 - mysqlclient - 连接数据库公开
- 89第三方库 - pysnooper - Print的高级版|调试|装饰器公开
- 90第三方库 - pynput - 控制键鼠公开
- 91第三方库 - python-docx - 操作word文档公开
- 92第三方库 - openpyxl - 操作Excel文档公开
- 93第三方库 - urllib2 - 请求库 - py3不存在了!!公开
- 94第三方库 - urllib3 - 请求库公开
- 95第三方库 - requests - 请求库公开
- 96第三方库 - requests-pkcs12 - p12请求公开
- 97第三方库 - selenium - Web自动化测试工具公开
- 98第三方库 - chromedriver - selenium的司机公开
- 99第三方库 - beautifulsoup4 - HTML解析库公开
- 100第三方库 - jieba - 结巴中文分词公开
- 101第三方库 - synonyms - 中文近义词公开
- 102第三方库 - 操作MySQL存储 - PyMySQL - 理解公开
- 103第三方库 - 操作MySQL存储 - PyMySQL - 写成类公开
- 104第三方库 - 操作MySQL存储 - PyMySQL增删改查公开
- 105第三方库 - 操作MySQL存储 - PyMySQL删表内容公开
- 106第三方库 - redis-py-cluster - Redis集群公开
- 107第三方库 - pymongo - 操作MongoDB公开
- 108第三方库 - bandit - 代码审计公开
- 109第三方库 - anytree - 树结构公开
- 110第三方库 - pyClamd - 杀毒公开
- 111第三方库 - PyInstaller - 打包Python程序公开
- 112第三方库 - Celery - 定时分布式任务执行公开
- 113第三方库 - pika - RabbitMQ公开
- 114第三方库 - asyncio - 异步方法公开
- 115第三方库 - Translate - 翻译公开
- 116自己写自己的库 - 理解公开
- 117web层 - web请求进入 - Django、Flask公开
- 118API层 - 外部API处理 - requests库公开
- 119biz层Service层 - 数据计算公开
- 120DAO层 - 数据库 - MySQL公开
- 121爬虫 - Instagram全部图片公开
- 122小工具 - mysql数据库设计转word公开
python运算
%E9%AD%94%E6%B3%95%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95-%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8.png&w=1920&q=85)
魔法方法汇总
Python中的魔法方法(也称为特殊方法或内置方法)是一系列以双下划线__开头和结尾的方法。这些方法在特定操作或内置操作时被自动调用,例如__init__()在对象创建时初始化对象,__len__()返回容器的长度,__str__()定义对象的字符串表示等。魔法方法允许开发者控制类的行为,使其与Python的数据类型和内置函数无缝协作,增强了类的功能性和灵活性。
python的魔法方法是通过__xx__()下划线来进行调用,是python已经有的方法,可以直接使用
| 分类 | 方法 | 说明 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 算术运算符 | __add__(self, other) |
定义加法的行为:+ | |
| 算术运算符 | __sub__(self, other) |
定义减法的行为:- | |
| 算术运算符 | __mul__(self, other) |
定义乘法的行为:* | |
| 算术运算符 | __truediv__(self, other) |
定义真除法的行为:/ | |
| 算术运算符 | __floordiv__(self, other) |
定义整数除法的行为:// | |
| 算术运算符 | __mod__(self, other) |
定义取模算法的行为:百分号 | |
| 比较运算符 | __lt__(self, other) |
定义小于号的行为:x < y 调用 x.lt(y) | |
| 比较运算符 | __le__(self, other) |
定义小于等于号的行为:x <= y 调用 x.le(y) | |
| 比较运算符 | __eq__(self, other) |
定义等于号的行为:x == y 调用 x.eq(y) | |
| 比较运算符 | __ne__(self, other) |
定义不等号的行为:x != y 调用 x.ne(y) | |
| 比较运算符 | __gt__(self, other) |
定义大于号的行为:x > y 调用 x.gt(y) | |
| 比较运算符 | __ge__(self, other) |
定义大于等于号的行为:x >= y 调用 x.ge(y) | |
__doc__() |
文档解释 | ||
__sizeof__() |
打印系统分配空间的大小 | ||
__class__() |
调用子类方法 |
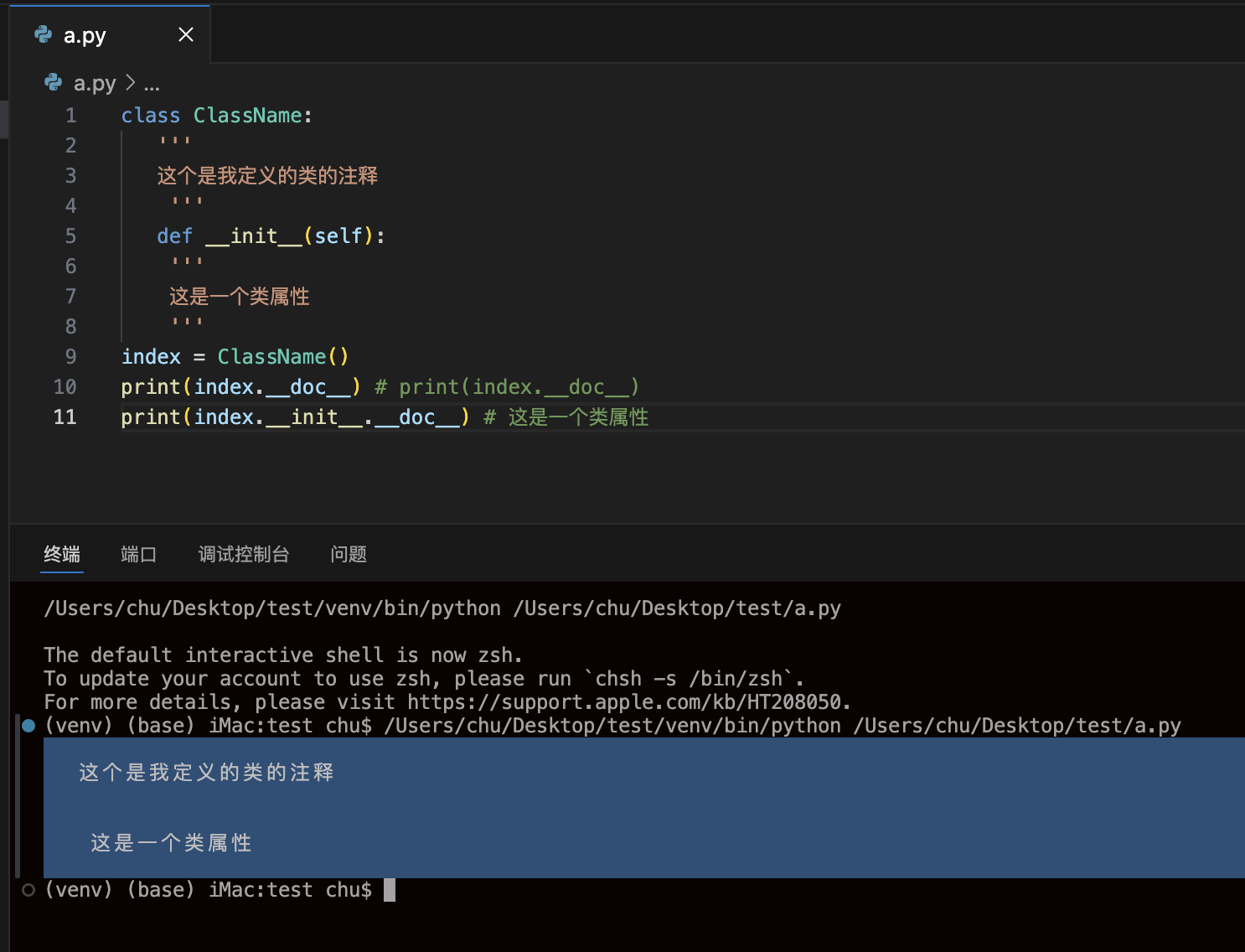
__doc__()类解释
class ClassName:'''这个是我定义的类的注释'''def __init__(self):'''这是一个类属性'''index = ClassName()print(index.__doc__) # print(index.__doc__)print(index.__init__.__doc__) # 这是一个类属性
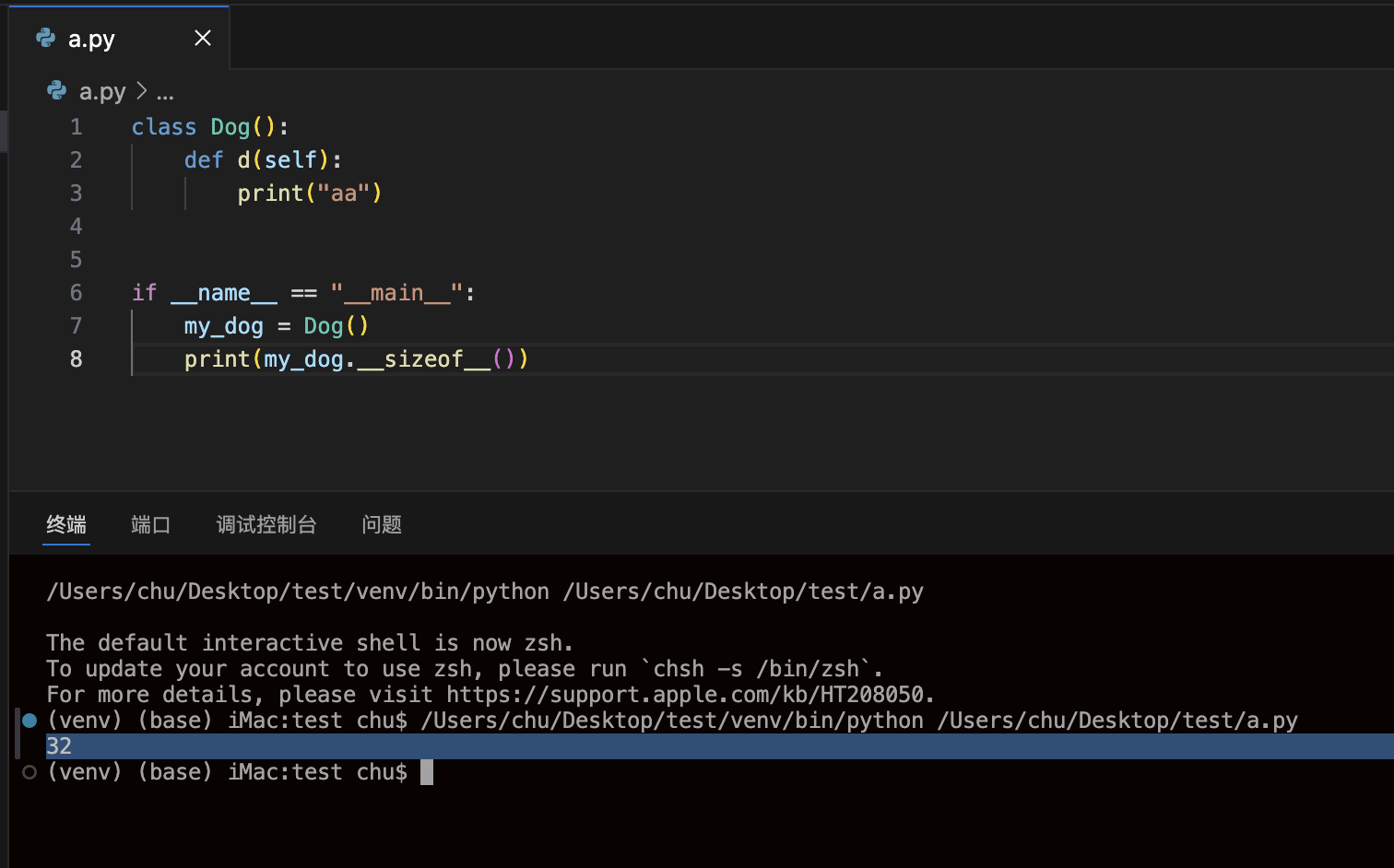
__sizeof__()打印系统分配空间的大小
class Dog():def d(self):print("aa")if __name__ == "__main__":my_dog = Dog()print(my_dog.__sizeof__())
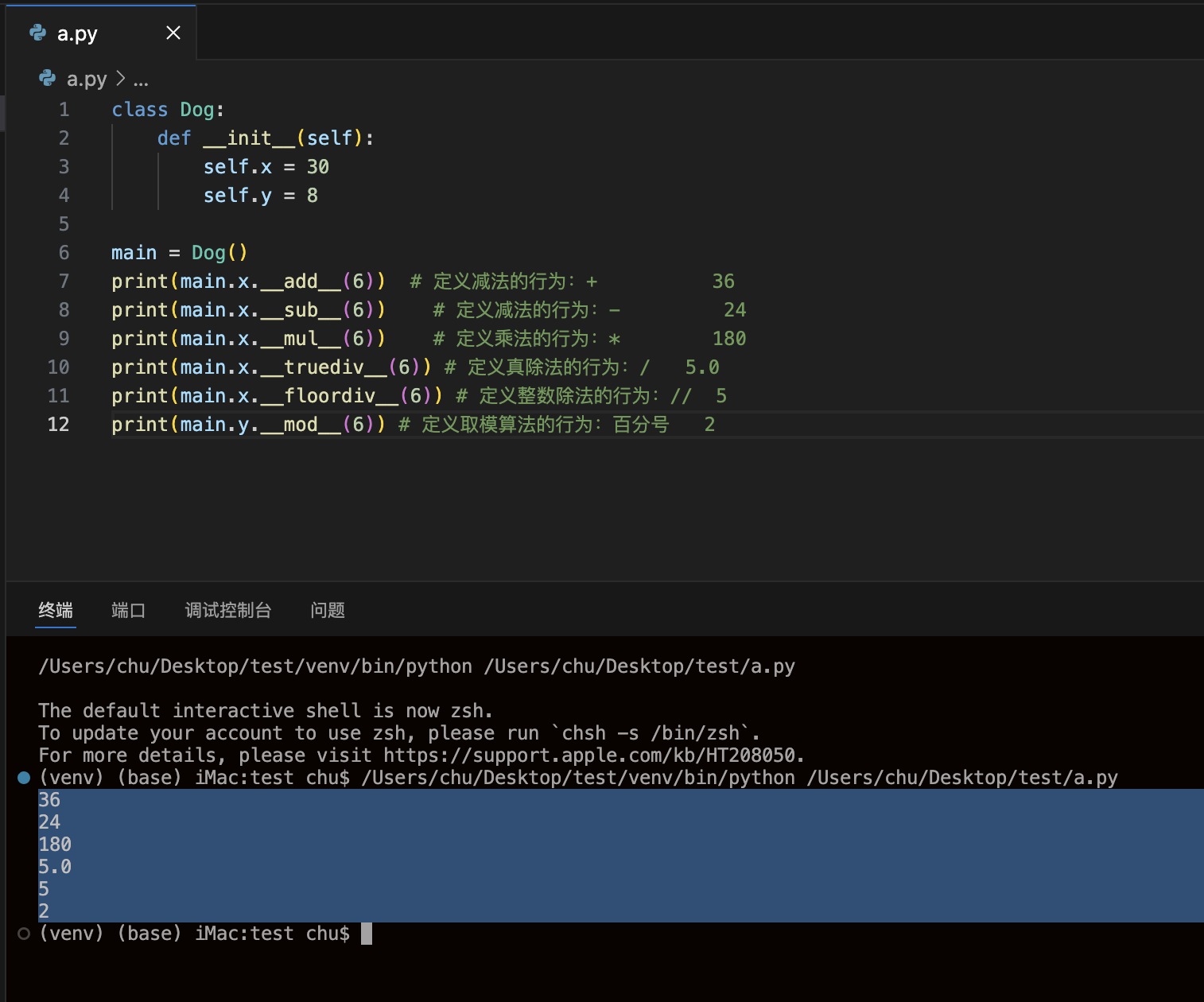
__add__(self, other)、__sub__(self, other)、__truediv__(self, other)、__floordiv__(self, other)、__mod__(self, other)
class Dog:def __init__(self):self.x = 30self.y = 8main = Dog()print(main.x.__add__(6)) # 定义减法的行为:+ 36print(main.x.__sub__(6)) # 定义减法的行为:- 24print(main.x.__mul__(6)) # 定义乘法的行为:* 180print(main.x.__truediv__(6)) # 定义真除法的行为:/ 5.0print(main.x.__floordiv__(6)) # 定义整数除法的行为:// 5print(main.y.__mod__(6)) # 定义取模算法的行为:百分号 2
__gt__()、__ge__()、__le__()、__lt__()、__eq__()、__ne__()
Python3中已经不能使用cmp()函数
import operator #首先要导入运算符模块operator.gt(1,2) #意思是greater than(大于)operator.ge(1,2) #意思是greater and equal(大于等于)operator.eq(1,2) #意思是equal(等于)operator.le(1,2) #意思是less and equal(小于等于)operator.lt(1,2) #意思是less than(小于)operator.__lt__(a, b)operator.__le__(a, b)operator.__eq__(a, b)operator.__ne__(a, b)operator.__ge__(a, b)operator.__gt__(a, b)
lt(a, b) 相当于 a < b
le(a,b) 相当于 a <= b
eq(a,b) 相当于 a == b
ne(a,b) 相当于 a != b
gt(a,b) 相当于 a > b
ge(a, b)相当于 a>= b
__class__()调用子类
class Foo(object):def create_new(self):return self.__class__()def create_new2(self):return Foo()class Bar(Foo):passb = Bar()c = b.create_new()print type(c) # We got an instance of Bard = b.create_new2()print type(d) # we got an instance of Foo

