- +在此添加单个AI新笔记
mongodb查询语句
find() 查询简介
MongoDB 的 find({},{}) 方法用于查询集合(Collection)中的文档(Document)。它接受一个查询对象来过滤文档,并返回一个迭代器,遍历所有匹配的文档。可以指定多个查询条件,支持字段匹配、范围查询等。使用时需注意查询效率,合理利用索引以优化性能。简单用法如下:
通过mongodb形式返回数据,具体命令例子为:
db.collection.find(query, projection)db.xx.find({查语句},{显示语句}){查语句}例子:{name:"小明"}{显示语句}例子:{name:1,_id:0}
其中:query 是一个文档,指定查询条件;projection 是可选的,用来指定返回字段。
使用find语句
使用find()命令前,可以用MONGOSH来查数据,以下是单击MONGOSH的默认画面:
单击MONGOSH,默认弹开test>,指的是进入了test数据库,需要use xx语句更换数据库
可以看见已经成功切换admin数据库,使用 - 用户管理 - admin库是mongodb的用户管理数据库。
现在可以使用在MONGOSH使用find()命令了
find()命令汇总
| 分类 | 名称 | 语法 | 命令 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全部 | 所有记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find(); |
注释1 |
| 全部 | 所有记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({}); |
注释1 |
| 全部 | 所有记录 | MySQL | select * from userInfo; |
|
| 1条 | 第一条数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.findOne(); |
|
| 选显示列 | 指定列name、age数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({}, {name: 1, age: 1}); |
注释2 |
| 选显示列 | 指定列name、age数据 | MySQL | select name, age from userInfo; |
|
| 选显示列 | 指定列name、age且age>25 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 25}}, {name: 1, age: 1}); |
|
| 选显示列 | 指定列name、age且age>25 | MySQL | select name, age from userInfo where age >25; |
|
| 条件等于= | age = 22的记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({"age": 22}); |
|
| 条件等于= | age = 22的记录 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where age = 22; |
|
| 条件不等于 | age = 22的记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({"age": {$ne:22}}); |
|
| 多条件 | name=zhangsan,age=22 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({name: "zhangsan", age: 22}); |
|
| 多条件 | name=zhangsan,age=22 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where name = "zhangsan" and age = "22"; |
|
| 条件大于>$gt | age > 22的记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 22}}); |
|
| 条件大于>$gt | age > 22的记录 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where age >22; |
|
| 条件小于<$lt | age < 22的记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$lt: 22}}); |
|
| 条件小于<$lt | age < 22的记录 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where age <22; |
|
| 条件大于等于>$gt | age >= 25的记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}}); |
|
| 条件大于等于>$gt | age >= 25的记录 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where age >= 25; |
|
| 条件小于等于<$lt | age<=25的记录 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$lte: 25}}); |
|
| 条件小于等于<$lt | age<=25的记录 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where age <= 25; |
|
| 多条件 | age>=23并且 age<=26 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 23, $lte: 26}}); |
|
| 列表条件 | 列表条件 | Mongo | db.users.find({city: {$in: ["New York", "Los Angeles"]}}) |
|
| 时间 | 时间 | Mongo | db.getCollection("A").find({ "createtime" : { "$gte" : ISODate("2021-05-28T00:00:00Z"), "$lt" : ISODate("2021-06-05T00:00:00Z") } }) |
|
| 包含 | name中包含 mongo的数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({name: /mongo/}); |
//相当于%% |
| 包含 | name中包含 mongo的数据 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where name like "%mongo%"; |
|
| 包含 | name中以mongo开头的 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({name: /^mongo/}); |
|
| 包含 | name中以mongo开头的 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where name like "mongo%"; |
|
| 排序sort | 按照年龄排序升序 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find().sort({age: 1}); |
|
| 排序sort | 按照年龄排序降序 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find().sort({age: -1},{ages: 1}); |
|
| 限制limit | 前5条数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find().limit(5); |
|
| 限制limit | 在5-10之间的数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find().limit(10).skip(5); |
注释3 |
| 限制limit | 第一条数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find().limit(1); |
|
| selecttop | 前5条数据 | MySQL | selecttop 5 * from userInfo; |
|
| skip | 10条以后的数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find().skip(10); |
|
| selecttop | 10条以后的数据 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where id not in (selecttop 10 * from userInfo); |
|
| selecttop | 第一条数据 | MySQL | selecttop 1 * from userInfo; |
|
| selecttop | 第一条数据 | MySQL | selecttop 1 * from userInfo; |
|
| 条数count() | 某个结果集的记录条数 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}}).count(); |
|
| 条数count() | 某个结果集的记录条数 | MySQL | select count(*) from userInfo where age >= 20; |
|
| 不重复distinct | 不重复数据 | Mongo | db.userInfo.distinct("name"); |
|
| 不重复distinct | 不重复数据 | MySQL | select distict name from userInfo; |
|
| or与 | or与 查询 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({$or: [{age: 22}, {age: 25}]}); |
|
| or与 | or与 查询 | MySQL | select * from userInfo where age = 22 or age = 25; |
|
| 查 | 按照某列进行排序 | Mongo | db.userInfo.find({***: {$exists: true}}).count(); |
|
| 查 | 按照某列进行排序 | MySQL | select count(***) from userInfo; |
注释1:
显示记录命令it:
默认每页显示20条记录,当显示不下的情况下,可以用it迭代命令查询下一页数据。
注意:键入it命令不能带;但是你可以设置每页显示数据的大小,用DBQuery.shellBatchSize= 50;这样每页就显示50条记录了。
注释2:
指定列name、age数据:
当然name也可以用true或false,当用ture的情况下和name:1效果一样,如果用false就是排除name,显示name以外的列信息。
_id默认显示,也可以-1不显示
注释3:
获得5-10之间的数据:
可用于分页,limit是pageSize,skip是第几页*pageSize
支持正则表达式查询命令
>db.test.find({x:/zhang/i}) // i忽略大小写ignore; /为表达式的开始和结束;>db.test.find({x:/san?/i}) // ?元字符规定其前导对象必须在目标对象中连续出现零次或一次>db.test.find({x:/^zh/}) // ^匹配字符串的开始>db.test.find({x:/san$/}) // $匹配字符串的结束>db.test.find({x:/san.hang/}) // .匹配任意一个字符(除换行符)>db.test.find({x:/sanwhang/}) // w匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字,只匹配一个字符>db.test.find({x:/sanshang/}) // s匹配任意的空白符,只匹配一个字符>db.test.find({x:/12dsaf/}) // d匹配数字,只匹配一个字符>db.test.find({x:/zhang/}) // 匹配单词的开始或结束,zhang开头(与^、$的用法相同)
数组查询命令
数据是数组的形式
db.scores.insertMany( [{ _id: 1, arrys_data: [ 82, 85, 88 ] },{ _id: 2, arrys_data: [ 75, 88, 89 ] }] )
>db.test.find({friends:"小A"}) //查询数组键friends中含“小A”元素的文档>db.test.find({friends:{$all:["FFF","小A"]}}) //$all数组按多个元素查询(不区分顺序)>db.test.find({friends:["小明1","小A"]}) //数组查询-精确匹配,顺序和内容都必须一致>db.test.find({"friends.0":"小明1"}) //friends.0按位置查询数组元素>db.test.find({"friends":{"$size": 2}}) //$size按数组长度查询数组,不能与$gt等同时使用>db.test.find({"friends":{"$size": 5}},{"friends":{$slice:2}}) //$slice显示数组前2条(-2显示最后两条)>db.test.find({"friends":{"$size": 5}},{"friends":{$slice:[0,2]}}) //$slice显示数组若干条。0开始位置,2显示数组数量>db.test.find({arrys_data:{$gt:10,$lt:80}}) //按范围查询数组-数组z:[5,25]被查出来,因为5<20且25>10>db.test.find({arrys_data:{"$elemMatch":{$gt:10,$lt:80}}}) //$elemMatch每个数组元素都满足: >10且<20
嵌套文档查询命令
>db.test.find({addr:{province:"河北省",city:"保定市"}}) //嵌套查询,精确匹配>db.test.find({"addr.province":"河北省","addr.city":"保定市"}) //嵌套查询,子文档中包含查询键就可以匹配>db.test.find({addr:{$elemMatch:{province:"河北省",city:"保定市"}}})
与或非 逻辑运算
逻辑运算主要就是三种类型: 与($and), 或($or), 非($not,$nor)在进行逻辑运算中最简单的就是$and ,用 “,”连接就可以了与($and) 语法:db.student.find({"age":{"$gt":33,"$lt":55}});或($or) 语法:db.student.find({"$or":[{"age":{"$gt":12}} , {"score":{"$lt":41}}]}).pretty();$nor 针对或的求反:db.student.find({"$nor":[{"age":{"$gt":43}} , {"score":{"$lt":78}}]}).pretty();
范围查询
"$in" (在范围之中), "$nin" (不在范围之中)"$in" 范例:db.student.find({"name":{"$in":["安安","梦梦"]}})"$nin" 范例:db.student.find({"name":{"$nin":["安安","梦梦"]}})
准备数据
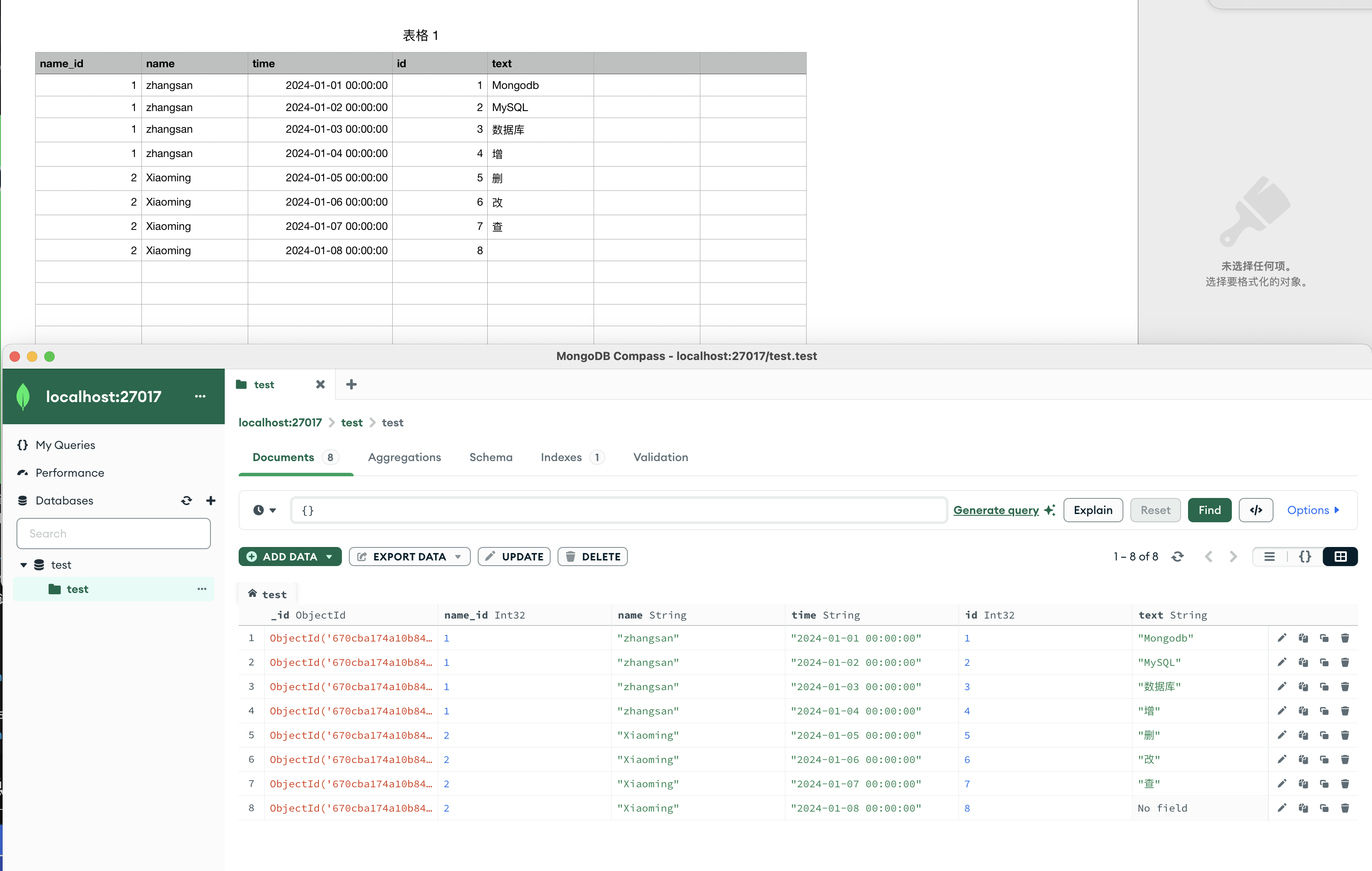
准备数据导入到Mongodb
可以看见id=8这里text数据空白,数据片里就没有这个text字段
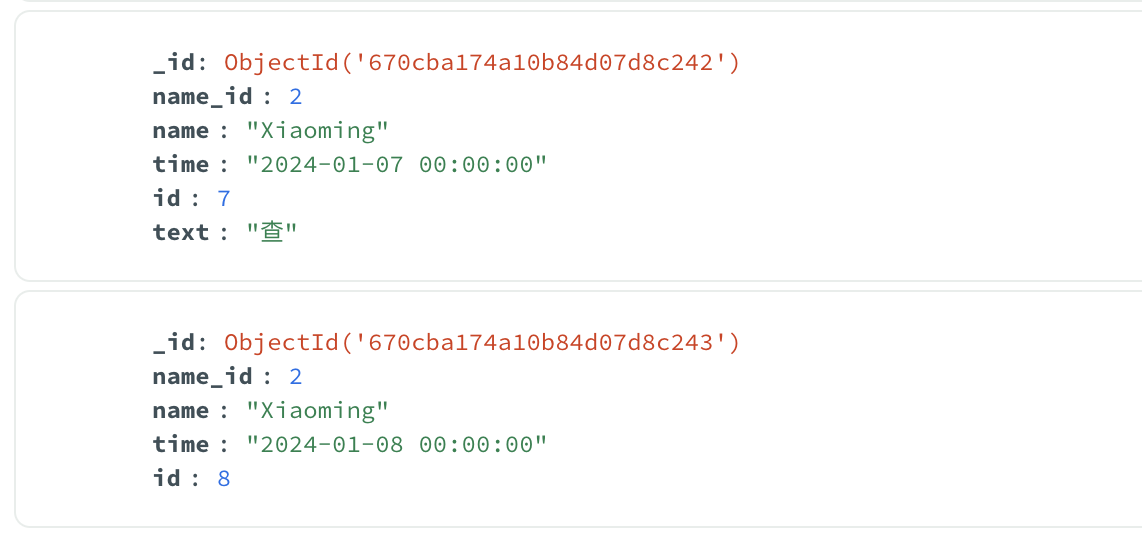
下方演示都是用这些数据
https://blog.csdn.net/ccysjy/article/details/127915483
全部所有记录db.userInfo.find();
db.userInfo.find();db.userInfo.find({});db.test.find();db.test.find({});
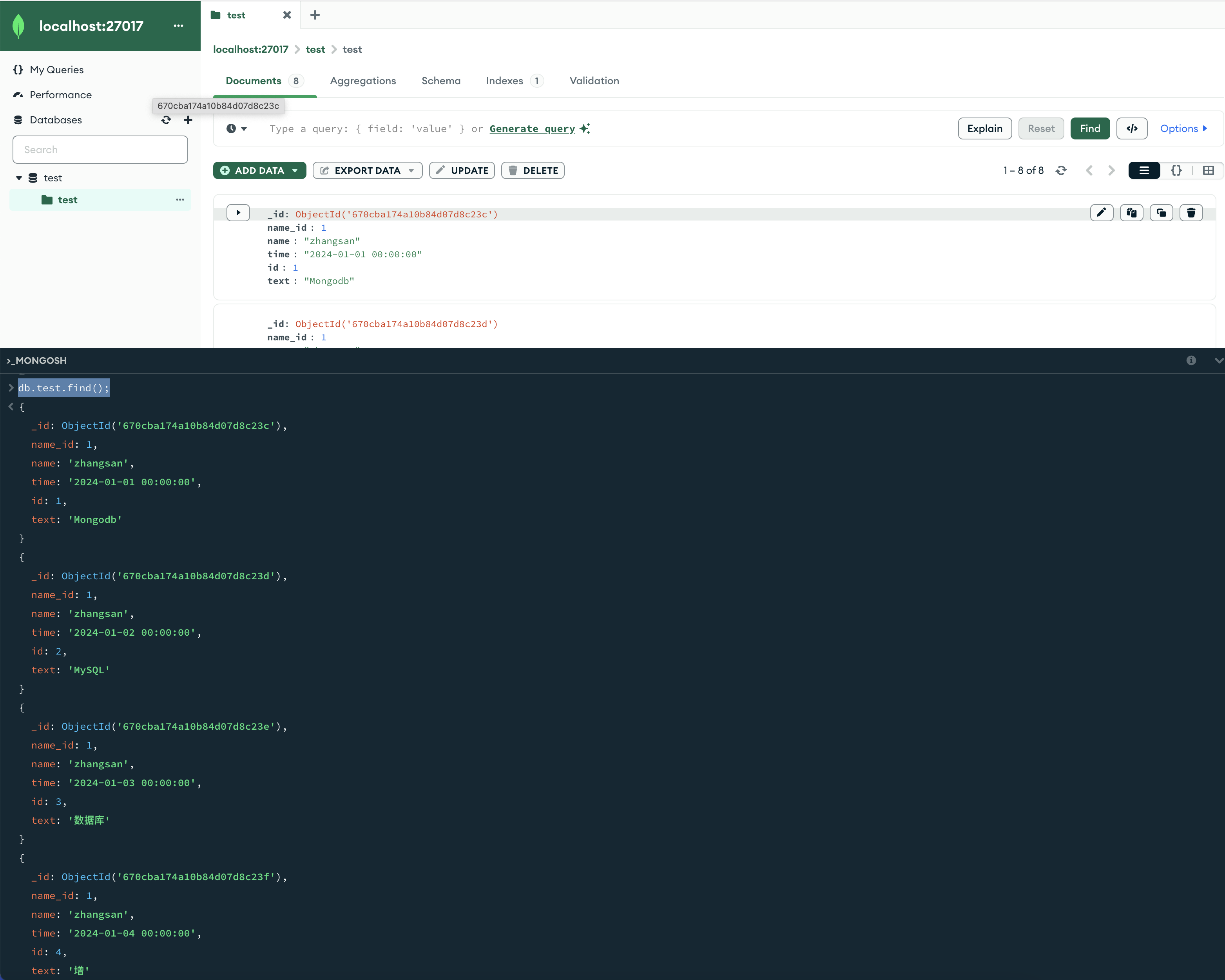
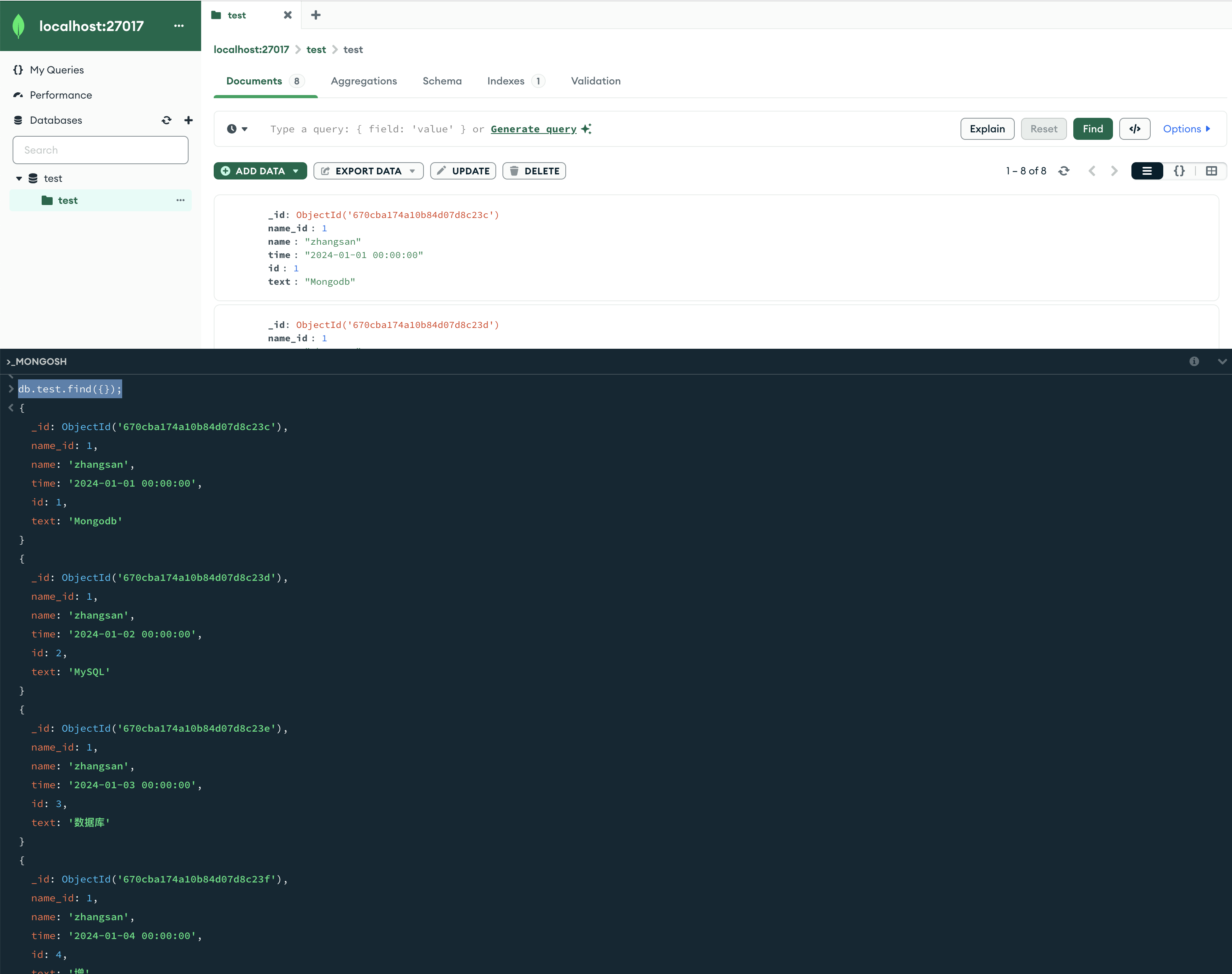
2条命令效果一样,都可以把全部的数据打印出来
第一条数据db.userInfo.findOne();
db.userInfo.findOne();db.test.findOne();
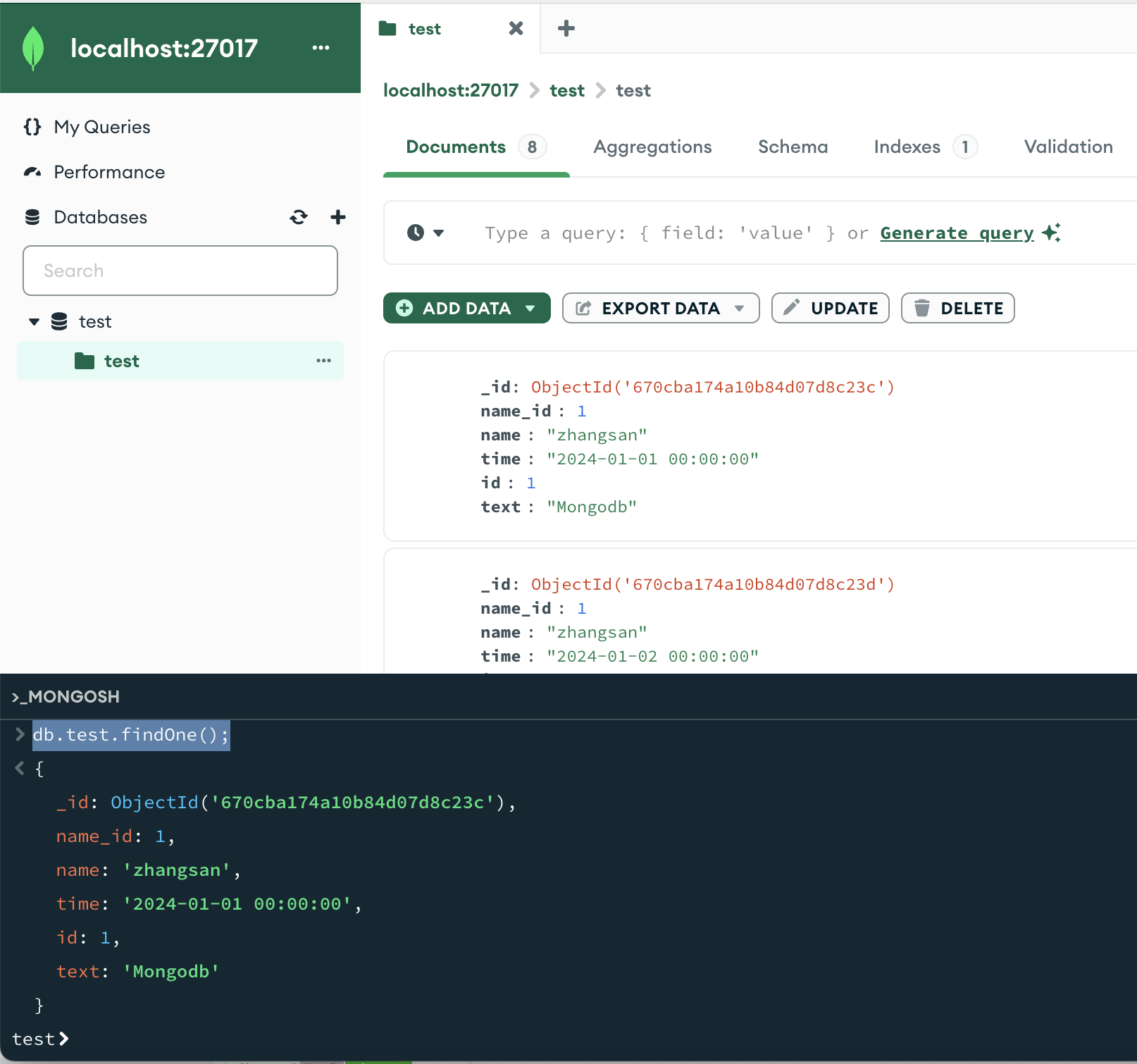
由于没有加上其他条件只,直接把第一条数据打印了出来
选显示列 指定列name、age数据 db.userInfo.find({}, {name: 1, age: 1});
db.userInfo.find({}, {name: 1, age: 1});db.test.find({}, {name: 1, id: 1});
这里选显示列,在第2个{}里写,1为显示,0为不显示。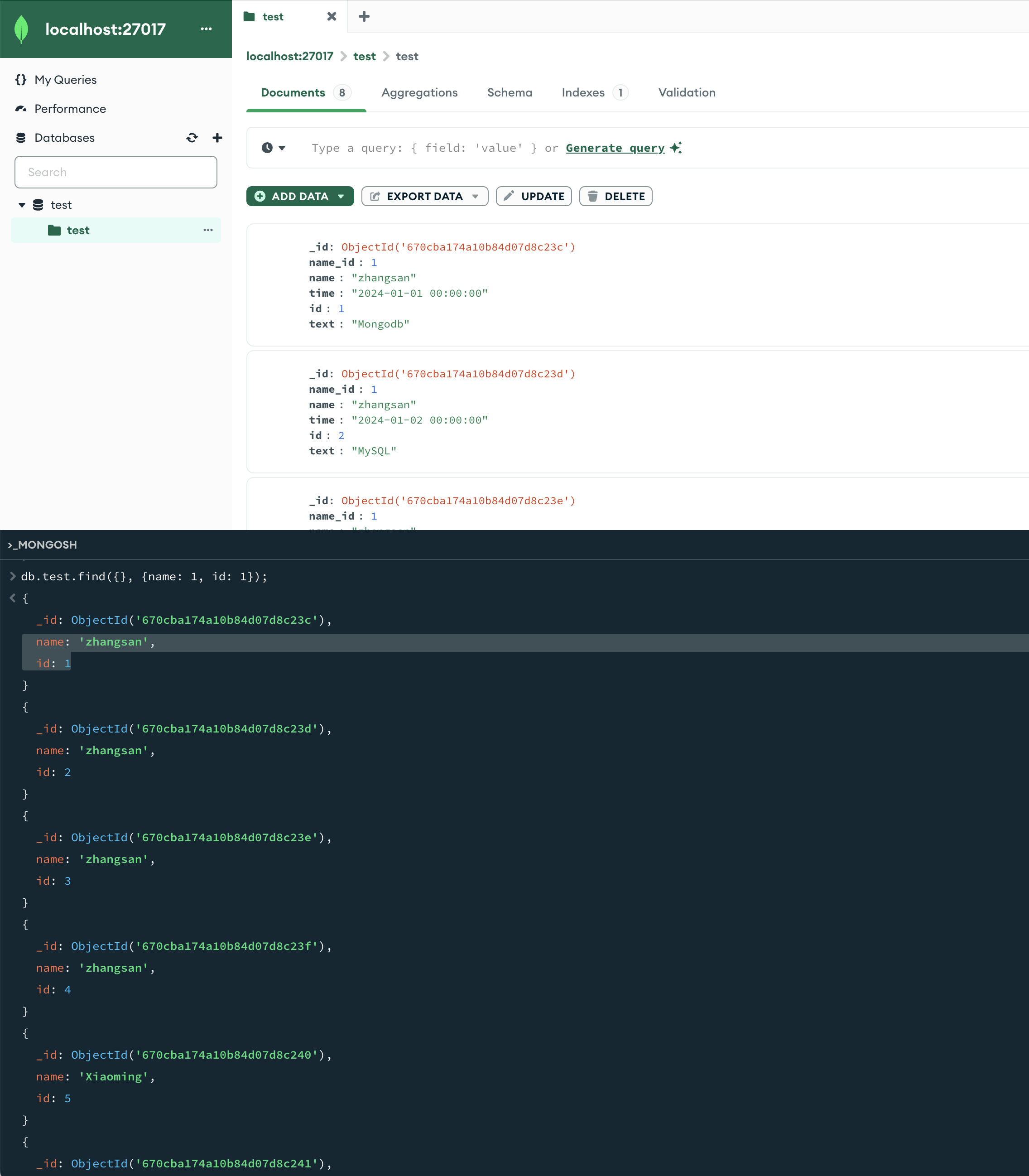
图片可以看见只显示了2列,分别是name列、id列
选显示列指定列name、age且age>25 db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 25}}, {name: 1, age: 1});
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 25}}, {name: 1, age: 1});db.test.find({id: {$gt: 5}}, {name: 1, id: 1});
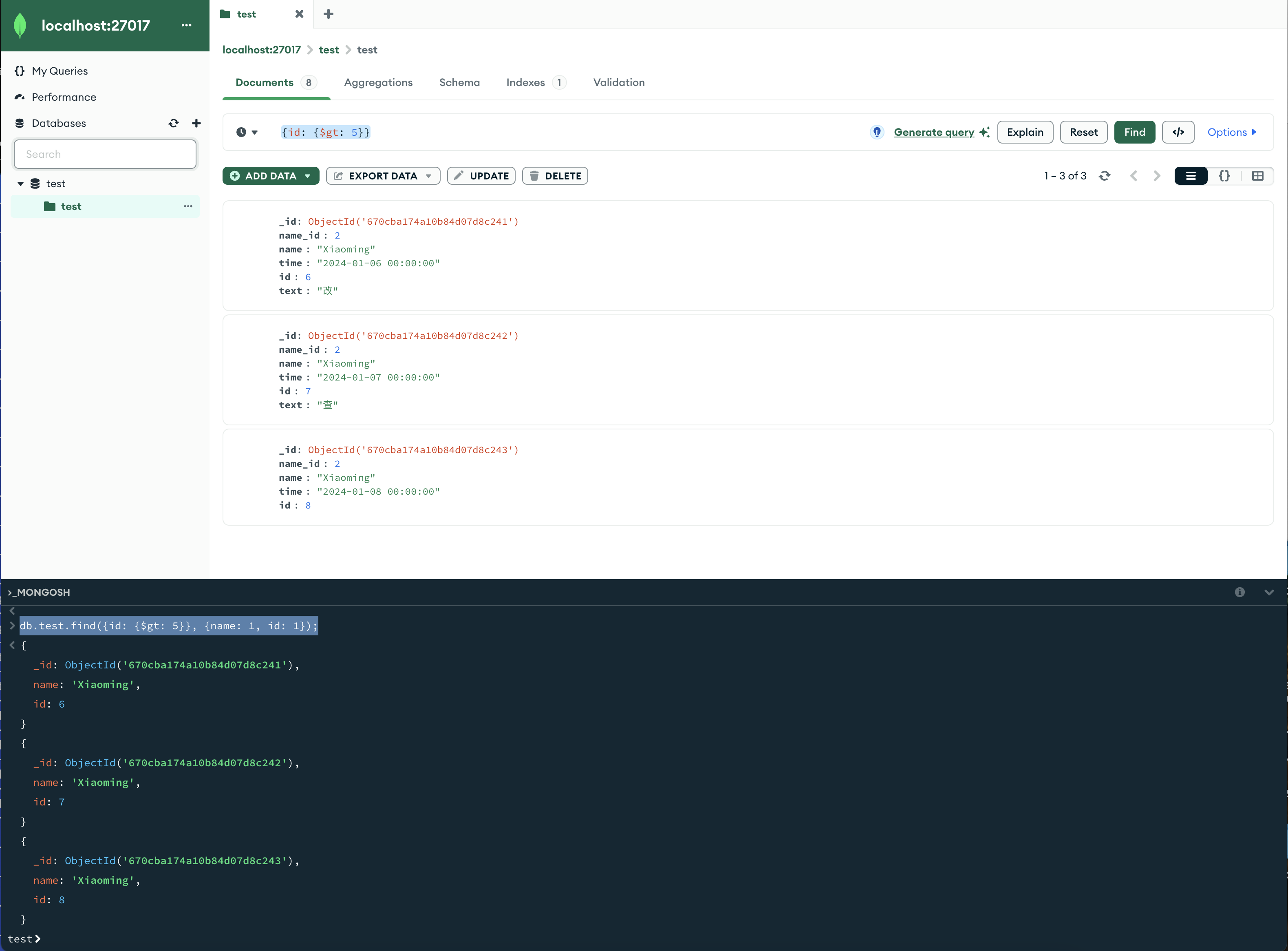
可以看见范围是id大于5的
条件等于= db.userInfo.find({"age": 22});
db.userInfo.find({"age": 22});db.test.find({"id": 3});
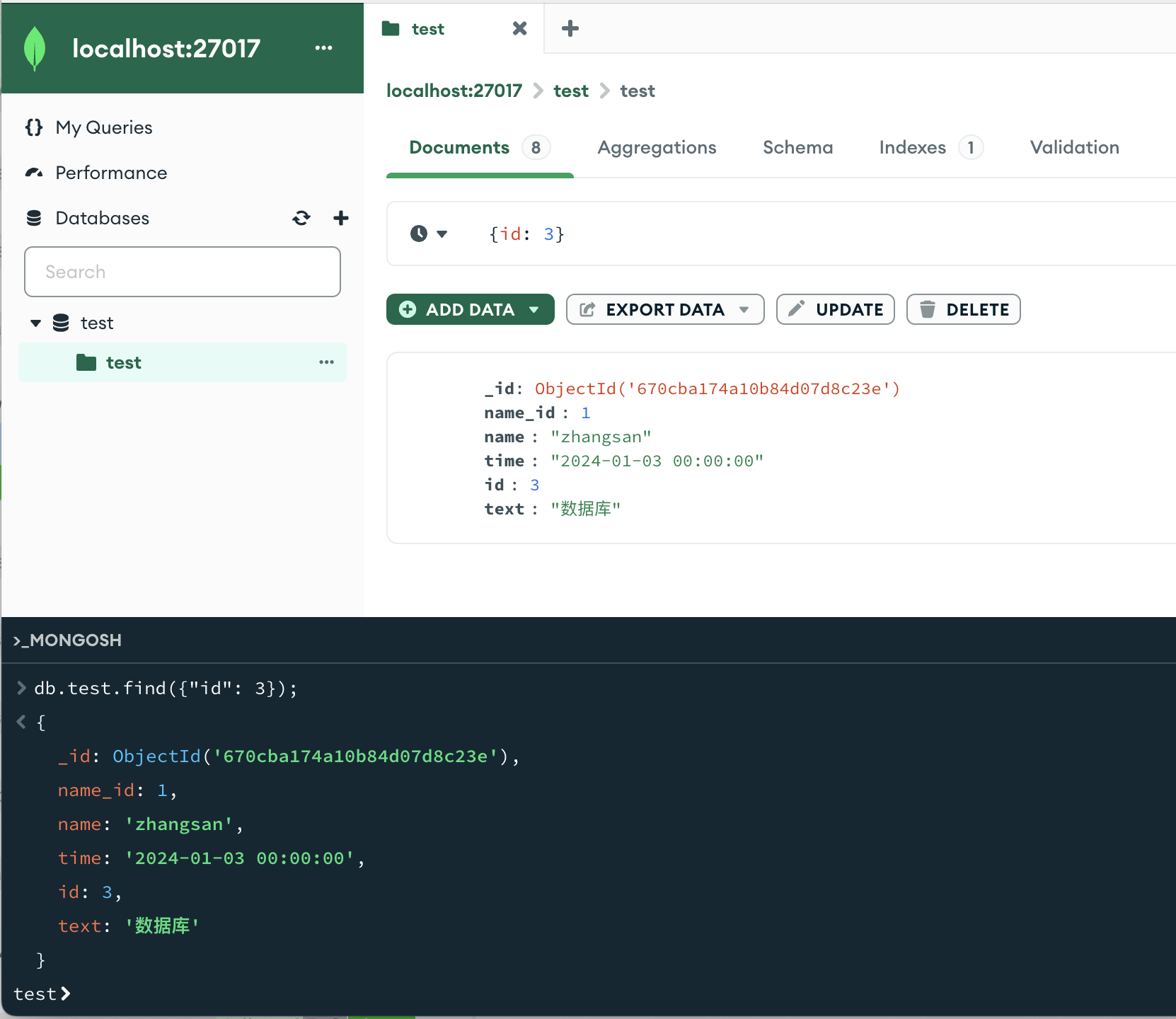
只获得1条数据
条件不等于 db.userInfo.find({"age": {$ne:22}});
db.userInfo.find({"age": {$ne:22}});db.test.find({"id": {$ne:3}});
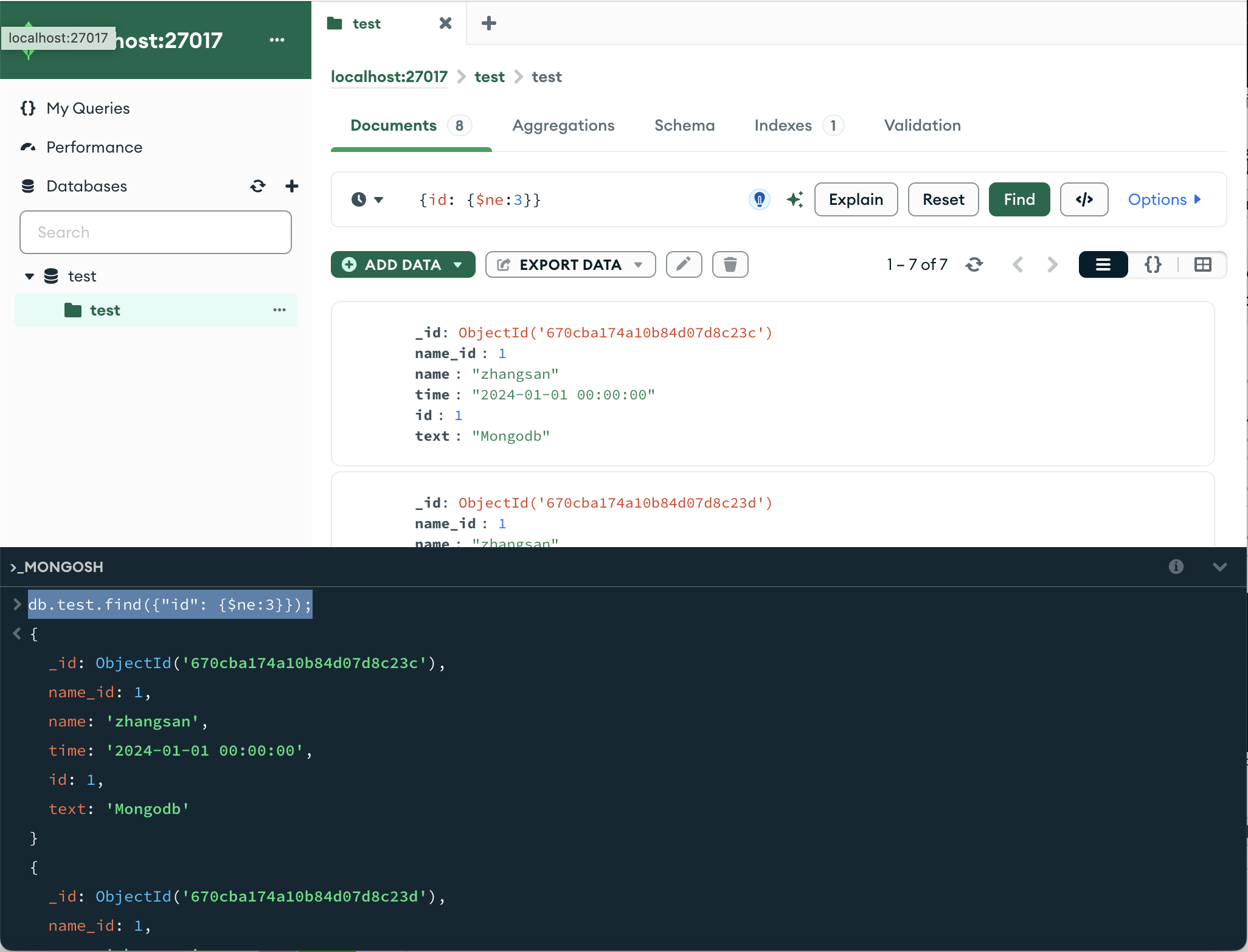
条件不等于可以看见可以获得7条数据


